While most people understand that IoT stands for the Internet of Things, most don’t know what the IIoT is. Before moving on to details on the differences, it is important to understand the underlying definition of each terminology.
IoT is a system of organized computing devices where each machine, object, and gadget has an IP address which enables them to transmit data from one network to another without depending on any human interface. As IoT evolves, we can witness how it keeps adding value to our lives. It is a broad and far-reaching concept that helps to increase efficiency at industrial, health and even domestic levels. With each passing day, humanity gets more involved in the web of IoT, and it is reshaping major aspects of our life, creating better experiences and compelling us to indulge much deeper into the hidden wonders of the digital realm.
It won’t be wrong to state that till this date, IoT is making our lives better. Even though some unfavorable aspects tag along, but there is always a way to amplify positivity while suppressing the negative ends if you have the desirable skills.
Whereas, IIoT is a sub-category of IoT and it links with industrial applications mainly such as the agricultural or the manufacturing sector. The Industrial Internet of Things enhances the manufacturing mechanisms by enabling the accessibility to more data, at a much higher speed and works on it even more efficiently than ever before. It brings in multiple advantages for that specific branch of industry. To be particular, IIoT or Internet 4.0 is the new face of manufacturing sector where technology combines with automation in entirely different ways.
No wonder there are some radical differences in the Internet of things and the Industrial internet of things. The first is general while the latter focuses specifically on industrial applications. The internet of things was meant to increase efficiency and improve the health/safety standards, but with the introduction of IIoT, it becomes more concerned with improving human experiences bringing an impact on all aspects of life.
As per the World Economic Forum, IIoT Report: “The Industrial Internet [of Things] will transform many industries, including manufacturing, oil, and gas, agriculture, mining, transportation, and healthcare. Collectively, these account for nearly two-thirds of the world economy.”
Apart from this basic difference, here are a few features that mark the difference of IIoT from IoT:
Fusing multiple domains
It won’t be wrong to claim that the prior internet revolution was meant to enhance the digital capacities and liberate humanity from shackles of animal power, but this one is different. It introduces a technological ground that infuses physical, digital and even the biological domains to impact multiple areas of the economy.
In these systems, the manufacturing mechanisms are not connected only to draw information from the physical world to the digital ground, but it goes an extra mile that is, it sets particular programs for data analysis too.
Virtual connectivity
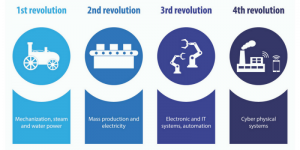
As the fourth industrial revolution sets foot and the world begins to witness major transformations, it is fundamental to point out the following features of IIoT:
- The internet-enabled smart equipment conducts interface with each another and even the human beings
- The virtual models and tools of data analysis make it easier to acquire and resolve the production problems
- The Cloud makes it possible to provide flawless service provision to the customers
- The modules of the factory can replace or expand at their own
Allows incredible insight
The machine-learning innovations and big data analytics of IIoT signify that with the collection of sensor data, people can gain incredible insight into the manufacturing procedures. The dynamic digital activity affects how the company engages with their customers and meets their changing preferences. IIoT enables the customer to hold a powerful position as they have the tool of connectivity. They want an affiliation with the product or the brand they are using which eventually leads to a change in which the customer-manufacturer interaction takes place. Indeed, the customer of this era asks for more access, information, and assistance. Such intense involvement of customers makes it possible for the manufacturers to identify the needs of their customers and helps them to provide a service-driven value.
CRM is a must for IIoT
Unlike IoT, the trends in IIoT display a shift towards customer-centric setup, which makes it mandatory for the company to incorporate a Customer Relationship Management software. It is a process whereby a program keeps a track and evaluates all interactions with the customers so that they can understand the changing needs as well as make sure that customers get an interactive experience. The IoT itself is mostly concentrating on making automotive innovations a part of human life. It works on the surface level of automation. The IIoT, on the other hand, is mainly shifting the industrial trends towards smart technology, internal connectivity and optimized quality of products.
Thereupon, the use of CRM software makes all these operations easier as manufacturers are empowered to collect and analyze data from multiple resources.
IIoT goes one step ahead and toils to bring a high-tech system in place. The new systems ask for deep knowledge of specific industries, data analytics, cyber security, and system integration. Moving into this ecosystem of intricate networks, it is important that we equip ourselves with knowledge of what differs IIoT from basic IoT and how can we improvise our competence.